What is a VPN, types of VPN how it work?
More and more employees are hearing that they are doing their work in the home office. They often use a so-called VPN connection for this. VPN stands for “Virtual Private Network”. A lot of people have heard of VPN, but what exactly is meant by it and how it works is known to only a few in details. We clarify here in this article in detail!
What is a VPN?
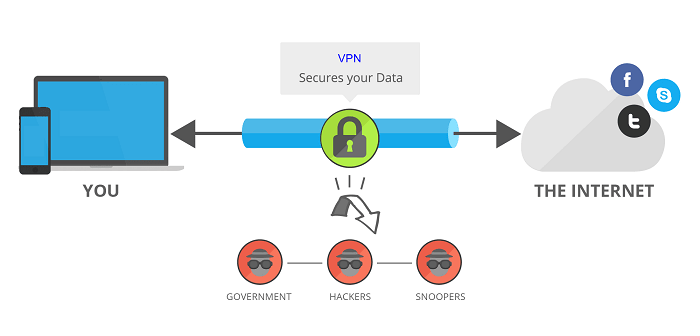
A VPN is a private network that enables you to create a secure connection to another network via Internet. Now-a-days, VPN’s are becoming very popular as it allows you to do work and connect different business online securely and one can easily access the business network from home also. Today we are facing lots of difficulties in work due to COVID-19 and businesses while giving the work to their employees to home use the VPN security as well.
Also Read: What is DMARC and How it Works and How to Access Dark Web on Tor
It is called virtual because it is not a separate physical connection, but you can use an existing network for it.
What are the advantages to using a VPN?
- Networks and clients around the world can be connected through a virtual private network.
- With a VPN, you get a secure connection via an unsecured network through the appropriate encryption. So it offers you increased security.
- Compared to other methods such as remote connections, it offers cost savings of up to 80 percent.
What is a VPN used for?
A virtual private network is primarily used because you need access to a network that you are not directly connected to. VPNs are primarily used for business purposes in order to ensure that employees can work securely at different locations or from their homes or offices.
But also in the private area you can use a VPN for different purposes:
- Increased privacy and security: with a VPN you can surf anonymously, hide your location and encrypt your data that is sent and received. For example, you can also bypass target-group-oriented advertising.
- Bypassing local locks: certain applications only work in certain areas. With a VPN connection you can access the offer of Netflix, Amazon Prime Video or Sky in Germany or any other country of your choice all over the world. So you can pretend to be in a certain location.
- In some countries, search engines like Google or social networks like Facebook or Instagram are blocked or monitored. With a VPN connection, you can also remove national blockages or filters of a country.
- Maybe you have installed a torrent client to download films and other content from the Internet. Even if these are legal downloads, there is always a feeling as to whether or not you have read or carefully read anything about the terms of use. A connection via a virtual private network is the best way to stay on the safe side.
What are the requirements for a VPN?
When using a virtual private network, you should pay particular attention to the following aspects:
- Security is usually the key factor that matters. Therefore, you should consider in advance what the VPN is used for and what security features it should offer. For example, should it only provide protection against research by the IP address or should it also protect against tracing by networked organizations and authorities?
- For all security, don’t forget performance. Complex encryption methods are secure, but they come at a cost of speed because they require a great deal of computing effort.
- When choosing the technology, you should pay attention to open standards so that you are not always tied to a manufacturer if any extensions are required. The network should also be scalable, i.e. allow higher numbers of users and bandwidths if necessary.
- The VPN should be able to be integrated into the existing network structure.

How does a VPN work?
When using a virtual private network, a so-called “tunnel” is created, i.e. a protected connection through which your data is sent to a remote server operated by the VPN provider. The remote server then sends your data to the source you want to connect to. This can be a website, for example, but also a third-party application on the company server. In the same way that you sent the data, you will receive the required data again: just through the tunnel.
What types of VPN are there?
There are three basic types of virtual private networks:
#1. Site to Site (from VPN gateway to VPN Gäteway)
This type is mostly used for networking multiple locations for companies. Several local networks from different branches are interconnected to form a network. Instead of using a dedicated line, which usually entails high costs, the respective connection to the Internet is used. An additional variant of this is the extranet VPN. Different companies are connected to each other in order to integrate certain services of other companies into their own network or to offer services for business partners or suppliers.
#2. Site to end (from VPN gateway to host)
You can use this type, for example, if employees from sales or from the home office have to access the company network. To do this, a VPN client must be installed on the employee’s computer in order to establish a VPN tunnel to the network. This type is often colloquially referred to as “remote access”. The goal of every site-to-end VPN should be to provide the safest possible access to the company network with as little financial and technical effort as possible.
#3. End to End
Here two servers are connected to each other via different locations. The corresponding VPN software must be installed on both sides. A typical application for this is, for example, remote desktop, i.e. the execution of application programs on a server, which are then operated and displayed on another computer.
What do you need to build a VPN?
What is required to set up a virtual private network depends primarily on which VPN type is to be used and which protocol is used for encryption.
What are the protocols for VPN?
When using virtual private networks, different protocols are used that are responsible for encryption.
The most common of these are:
#1. IKEv2
This is the latest protocol. It has the advantage that it is stable and easy to set up and can be used very well, especially on mobile devices. Unfortunately, it is still not supported by all platforms.
#2. OpenVPN
OpenVPN is open source and extremely versatile. Most VPN experts recommend it primarily because it offers the highest security standard. However, it requires a lot of resources, which is why it does not work as quickly as the other protocols in direct comparison. However, the speed always depends on which hardware you use, so you should pay particular attention to this when using OpenVPN.
#3. L2TP / IPsec
The so-called Layer 2 tunnel protocol is very easy to set up and at the same time offers you a high level of security. However, it is a bit older and is therefore no longer properly supported by all new devices. It is also one of the slower protocols. The problem is that Edward Snowden has pointed out that the protocol has now been cracked. This has caused an enormous loss of trust.
#4. PPTP
The point-to-point tunneling protocol has a pretty bad reputation because it has been levered out under laboratory conditions. Basically, however, it offers a very fast connection, is above all easy to set up and is supported by most devices. But it is now very outdated and can no longer keep up with modern standards. It should therefore be avoided, especially for use in companies.
Depending on the area of application, all protocols have different properties and special features. Technology has made a big leap forward in recent years. As a normal user, you no longer need to work through technical terms and can usually click through the installation very easily. You should still build up a little background knowledge about the differences. In summary, one can say: OpenVPN and IKEv2 are alternatives for professional use. L2TP / IPsec also work well when implemented correctly, but shouldn’t really be your first choice. You should avoid TP altogether, as it offers you very little protection against unwanted access compared to today’s security requirements.
Conclusion
In summary: a virtual private network is always a good thing when it comes to establishing a secure connection. However, the choice of the right provider and the right technology always depends on the area of application. In any case, companies should pay more attention to security, since company data is confidential and should not get into unauthorized hands. For home use, on the other hand, it’s all about staying anonymous, leaving no traces on the Internet and being able to simulate different locations. Above all, it is possible to set it up without much financial and technical effort.